CSWIP 3.1 QUESTION AND ANSWER SERIES

[BUY] CSWIP 3.1 Learning Package
(145mb) Books & Chapter wise Questions (General Paper + Technical Paper) and Answers. Examination notes on Practical Examination of Plate/Pipe CSWIP 3.1 Learning Presentation
$72.00
CSWIP 3.1: Question with Answer and Explanation – Part 1
CSWIP 3.1: Question with Answer and Explanation – Part 2
CSWIP 3.1: Question with Answer and Explanation – Part 3
CSWIP 3.1: Question with Answer and Explanation – Part 4
CSWIP 3.1: Question with Answer and Explanation – Part 5
CSWIP 3.1: Question with Answer and Explanation – Part 6
CSWIP 3.1: Question with Answer and Explanation – Part 7
CSWIP 3.1: Question with Answer and Explanation – Part 8
CSWIP 3.1: Question with Answer and Explanation – Part 9
CSWIP 3.1: Question with Answer and Explanation – Part 10
CSWIP 3.1: Question with Answer and Explanation – Part 11
CSWIP 3.1: Question with Answer and Explanation – Part 12
CSWIP 3.1: Question with Answer and Explanation – Part 13
CSWIP 3.1: Question with Answer and Explanation – Part 14
CSWIP 3.1: Question with Answer and Explanation – Part 15
CSWIP 3.1: Question with Answer and Explanation – Part 16
CSWIP 3.1: Question with Answer and Explanation – Part 17
CSWIP 3.1: Question with Answer and Explanation – Part 18
CSWIP 3.1: Question with Answer and Explanation – Part 19
CSWIP 3.1: Question with Answer and Explanation – Part 20
1) For ultrasonic testing, which of the following statements is true?
| a. | It is easy to identify all defects |
| b. ( answer ) | The equipment should be calibrated before use |
| c. | The equipment cannot be automated |
| d. | Sound waves will not travel through copper |
UT Disadvantages:
- Trained and skilled operator required
- Requires high operator skill
- Good surface finish required
- Defect identification
- Couplant may contaminate
- No permanent record
- Calibration Required
- Ferritic Material (Mostly)
Why:
Calibration refers to the act of evaluating and adjusting the precision and accuracy of measurement equipment. In ultrasonic testing, several forms of calibration must occur. First, the electronics of the equipment must be calibrated to ensure that they are performing as designed. This operation is usually performed by the equipment manufacturer and will not be discussed further in this material. It is also usually necessary for the operator to perform a “user calibration” of the equipment. This user calibration is necessary because most ultrasonic equipment can be reconfigured for use in a large variety of applications. The user must “calibrate” the system, which includes the equipment settings, the transducer, and the test setup, to validate that the desired level of precision and accuracy are achieved. The term calibration standard is usually only used when an absolute value is measured and in many cases, the standards are traceable back to standards at the National Institute for Standards and Technology.
2) Which of the following standards is concerned with welder approval?
| a. | BS EN 499 |
| b. | BS EN 288 |
| c. | BS EN 22553 |
| d. ( answer ) | BS EN 287 |


3) The WPS calls for a root gap to be between 2 and 3mm, the actual measured gap is 4mm, … of action would you like?
| a. | Accept it as its only 1mm |
| b. ( answer ) | Reject it |
| c. | The welder will decide, if it fails it will be his problem |
| d. | The welder insists he can weld the butt joint easily so let him go ahead |
Pls understand that:
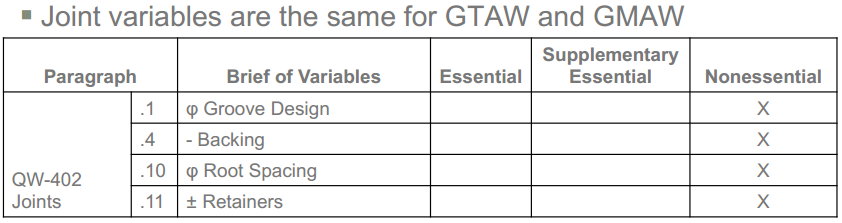
- With Welding inspector position: We have follow Approved WPS stricly! Any difference with WPS will be rejected. But:
- With Welding engineer: it can cosider to checked again. For ex: if it is checked follow ASME IX: root spacing is Nonessential –> can accept.
4) What is the abbreviation for a Welding Procedure Specification that has been written for the purpose of qualifying a Weld Procedure Test weld?
| a. | WPS |
| b. ( answer ) | pWPS |
| c. | uWPS |
| d. | pWPT |
Pls see attached link: WPS understanding.
- pWPS: Some codes, such as AWS D1.1, allow “Prequalified WPS”, whereby it is established that the WPS written per code will produce welds with correct mechanical and metallurgical properties. It is NOT NEED to prepare a PQR in such cases. However, the pre-qualified WPS have a specified range (TABLE 3.X) of parameters under which the weld must be produced. When welding variables fall outside these ranges, a WPS with supporting PQR must be prepared.
- PQR: is a record of the weld data used to weld a test coupon. It also contains the test results of the tested specimens. The completed PQR shall document all the essential when required supplementary essential variables for each welding process used during the welding of test coupon. Non essential variables used during the welding of the coupon may be recorded.
- WPS: is a written document that provides direction to the welder or welding operator for making production welds in accordance with code requirements. The completed WPS shall describe all the essential , non essential and when required supplementary essential variables for each welding process used in the WPS.
One question: between WPS & PQR – which one have first?
- To come out a WPS we need follow these below steps – 5 steps:
- Five Step Process to Qualify a Welding Procedure
1. Understand the intended application for which the WPS will be used
2. Develop a draft procedure
3. Make a qualification weld
4. Test the qualification weld
5. Write up the WPS - Step No. 2: we can understand it is pWPS ( prequalified WPS )
- Step No. 3: it is PQR
So, between WPS & PQR: PQR have first.
5) How are the lengths of tack welds during assembly and fit up determined?
| a. | By the welders as they have extensive knowledge |
| b. ( answer ) | The fabrication specification will give minimum tack length requirements |
| c. | The fabrication drawing will give all the information |
| d. | Any length of tack weld will do for assembly |
For information:
Qualification of tack welds, a topic that is being interpreted differently by various companies. Tack welds on EXC2, EXC3 and EXC4 components are required to be welded in accordance with a qualified WPS. Tack welds are to be a maximum length of 4x the thickness of the thicker part or 50mm “…unless a shorter length can be demonstrated as satisfactory…”.
6) What does the term WPS mean?
| a. | Weld productivity specification |
| b. | Weld production scheme |
| c. ( answer ) | Welding procedure specification |
| d. | Work productivity standard |
Pls see question No. 4
7) What does the term WPQR mean?
| a. | Weld productivity quality review |
| b. | Weld productivity quality requirements |
| c. ( answer ) | Welding procedure qualification record |
| d. | Work production quantity review |
Pls see question No. 4
8) Is it always necessary to preheat the base material before welding?
| a. | Not on a sunny day |
| b. ( answer ) | Only in accordance with the WPS |
| c. | If the equipment is available it must be used |
| d. | If using cellulosic rods these will provide enough heat |
It depens on the thickness of material / type of material.
9) Which of the following would not be required to be checked before welding?
| a. | The welding consumables |
| b. | The weld root gap |
| c. ( answer ) | PWHT temperature range |
| d. | The weld preparation |
PWHT: POST WELD HEAT TREATMENT – are used to change the properties of the weld metal, controlling the formation of crystalline structures.
PWHT is a mandatory requirement when certain criteria are met, the main one being the thickness. BS EN 13445 and BSPD 5500 require that joints over 35mm thick are PWHT’d, ASME VII above 19mm. If, however, the vessel is to enter service where stress corrosion is a possibility, PWHT is mandatory, irrespective of thickness. The soak time is also dependant on thickness. As a very general rule this is one hour per 25mm of thickness; for accuracy, reference must be made to the relevant specification.
Post Weld Heat Treatment (PWHT):
So what does the term ‘post weld heat treatment’ mean? To some engineers it is a rather vague term that is used to describe any heat treatment that is carried out when welding is complete. To others however, particularly those working in accordance with the pressure vessel codes such as BS PD 5500, EN 13445 or ASME VIII, it has a very precise meaning. When an engineer talks of post weld heat treatment, annealing, tempering or stress relief it is therefore advisable.
10) How do we determines what the correct weld preparation (root gap, root face, included angle) should be?
| a. ( answer ) | By consulting the WPSs |
| b. | The fabrication drawing will give all the information |
| c. | The welder will decide |
| d. | The inspectors will recommend what is suitable |
Pls see next part:


Very useful things
LikeLike